What is Hep C
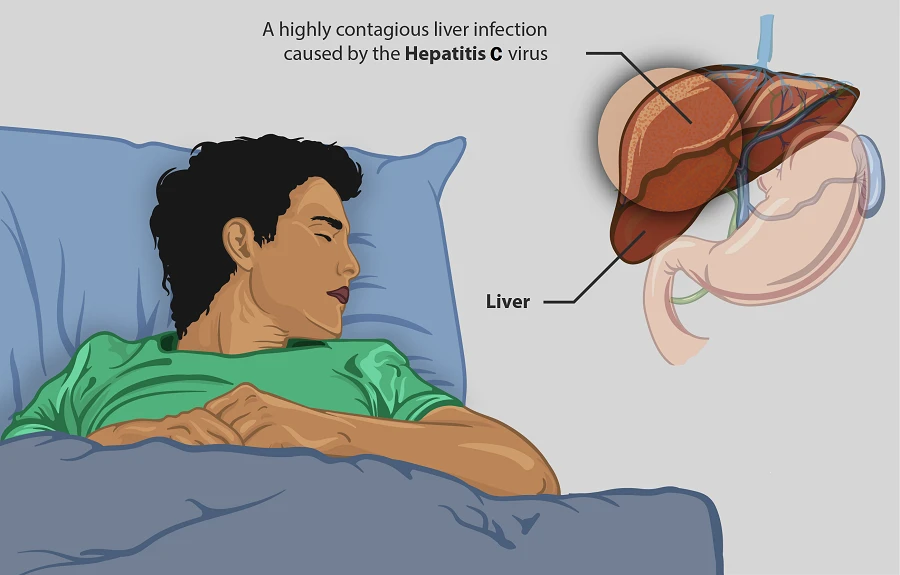
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which is transmitted through contact with infected blood. The infection can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer if left untreated. Therefore, finding a cure for hepatitis C is crucial for preventing these serious complications.
In the past, treatment for hepatitis C involved a combination of medications, such as interferon and ribavirin, which could cause severe side effects and were not always effective. However, in recent years, new medications have been developed that offer a cure for hepatitis C with few side effects.
Treatment
The treatment of hepatitis C involves using direct-acting antiviral drugs (DAAs) to target specific proteins in the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and prevent it from replicating in the liver. There are several types of DAAs, each of which targets a different protein in the HCV. Here is a brief overview of the different types of DAAs:
- NS5A inhibitors: NS5A is a protein that is essential for the replication of the HCV. NS5A inhibitors are a type of DAA that block this protein, preventing the virus from replicating. Examples of NS5A inhibitors include ledipasvir, velpatasvir, and daclatasvir.
- NS5B inhibitors: NS5B is another protein that is involved in the replication of the HCV. NS5B inhibitors are a type of DAA that block this protein, preventing the virus from replicating. Examples of NS5B inhibitors include sofosbuvir, dasabuvir, and elbasvir.
- Protease inhibitors: The NS3/4A protease is an enzyme that is needed for the HCV to replicate. Protease inhibitors are a type of DAA that block this enzyme, preventing the virus from replicating. Examples of protease inhibitors include grazoprevir, paritaprevir, and simeprevir.
- Combination therapies: Combination therapies involve using two or more types of DAAs together to provide a more effective cure for hepatitis C. Examples of combination therapies include:
- Harvoni: This is a combination of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir that targets both the NS5A and NS5B proteins.
- Epclusa: This is a combination of sofosbuvir and velpatasvir that targets both the NS5B and NS5A proteins.
- Mavyret: This is a combination of glecaprevir and pibrentasvir that targets both the NS3/4A protease and the NS5A protein.
The specific medication or combination of medications used to treat hepatitis C depends on several factors, including the genotype of the virus (there are several different types of HCV), the stage of the infection, and the individual’s overall health.
In general, treatment with DAAs for hepatitis C involves taking one or more medications daily for a period of 8 to 12 weeks. During this time, the medications work to eliminate the HCV from the body. Blood tests are used to monitor the progress of the treatment and determine if the virus has been eliminated.
Studies have shown that treatment with DAAs can cure hepatitis C in over 95% of cases. This means that the virus is completely eliminated from the body, and the individual is no longer at risk for developing liver damage or other complications associated with hepatitis C.
Promising Outlook
there are many reasons to have a positive outlook towards the cure of hepatitis C. Highly effective treatments, short treatment duration, fewer side effects, and affordable treatment options are just a few of the reasons why the outlook for people with hepatitis C is better than ever. With the right treatment, people with hepatitis C can achieve a cure and live a healthier, happier life.
Citation
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hcv/index.htm
Featured pic: https://tinyurl.com/h6k3be27


3 thoughts on “Hepatitis C cure: How DDA drugs are revolutionizing the treatment!”