Overview
In recent years, the fastest-growing vegan milk substitute has been oat milk. It is a dairy-free substitute for cow’s milk. Oat milk generally benefits people who are lactose, nut, soy, or gluten intolerant, as well as those who follow a plant-based or vegan diet.
Oat Milk Production
Water and oat flour are the two major components of oat milk.
The additional ingredients, which may include vegetable oil, salt, stabilizers, vitamin and mineral blends, sweeteners, and flavors, vary between brands.
The standard method of producing oat milk is fairly easy.
To begin, the rolled oats are mixed with water to form a slurry. This combination is hydrolyzed, which breaks down the starch and prevents gelatinization and thickening at high temperatures. Filtration is the final stage.
Following ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing, the finished product becomes shelf-stable and can be stored at room temperature (in sealed packaging) until the best-before date. UHT oat milk must be refrigerated once the seal is opened.
How to Make Oat Milk at Home
Oat milk is quite simple to produce at home. Furthermore, creating your own preparation enables you to select the components and eliminate additives or thickeners commonly found in commercial brands of oat milk. You may also use certified gluten-free oats to make it gluten-free.
However, a homemade version may not include as many nutrients as store-bought fortified treated oat milk. To create oat milk, combine one cup of rolled or steel-cut oats and three cups of water in a blender. To separate the oat milk from the oats, strain the mixture through a cheesecloth. Once made, refrigerate it in a glass bottle for up to five days.
You may try adding a teaspoon of vanilla or cinnamon essence, a few dates, maple syrup, or honey to enhance flavor.
How does oat milk’s nutritional profile compare to that of cow’s milk
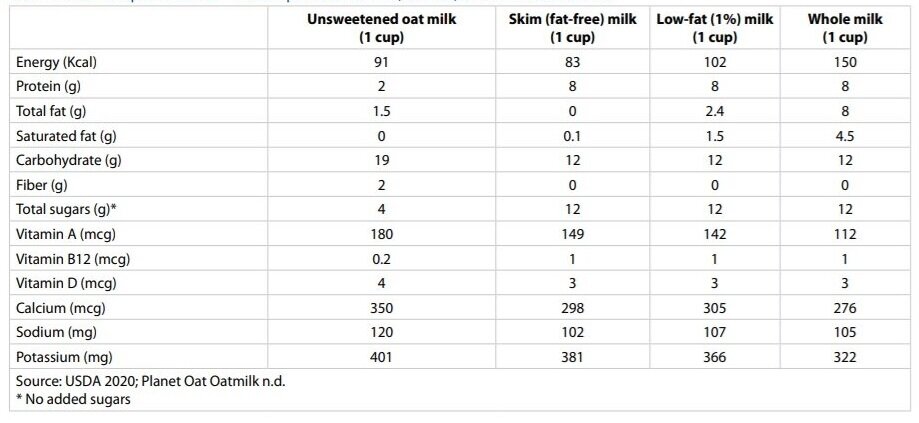
Most unsweetened oat milks has around 90 calories per 1 cup (8 oz) serving, which is less than whole and low-fat cow’s milk and somewhat more than skim (fat-free) milk. However, the nutritional profile of oat milk differs from brand to brand.
Whole and low-fat cow’s milk have less saturated and total fat than oat milk. In comparison to oat milk, which often has additional oil, skim cow’s milk is fat-free. In terms of protein content, oat milk contains much less protein than cow’s milk. Oat milk has more carbs than cow’s milk, with starch and 4 g of sugar. In addition, oat milk has 2 g of fiber per serving, whereas cow’s milk contains none.
Many commercially available oat milks are mildly fortified with calcium, riboflavin, and vitamins A, D, and B12. The salt level of oat milk is comparable to that of cow’s milk.
Exploring Oat Milk Benefits for Your Health
- Oats include beta-glucan, a kind of fiber that has been found to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol. In patients with type 2 diabetes, eating oats decreases blood cholesterol, as well as after-meal blood glucose and insulin, a hormone that regulates the quantity of glucose in the blood. However, because fiber contents vary from brand to brand due to different processing techniques, it may be difficult to ingest enough beta-glucan fiber to accomplish these benefits. It’s crucial to remember that the health benefits of oat milk haven’t been well-researched.
- Hence, it is wiser to enjoy oat milk incorporated as part of a healthy, well-balanced diet that also contains a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, healthy fats, and protein.
- A comprehensive medical study concluded that in adult males, 5 weeks of oat milk consumption reduced blood cholesterol and LDL cholesterol.
- The oat milk has none of the major eight known allergens—dairy, eggs, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, fish, crustacean shellfish, and soybeans—and is thus a suitable alternative for people who are allergic to any of these foods.
- Oats also don’t contain gluten, a protein that celiac disease and gluten sensitivity people must avoid. However, some brands produce oat milk in facilities that also process wheat and dairy, where gluten cross-contamination is possible.
- Oat milk is also lactose-free, making it an ideal choice for people who have lactose sensitivity.
- Contrary to cow’s whole milk, oat milk has far fewer calories. It is also known to provide a sense of satiety as it is laden with carbs.
- Oat milk is suitable for vegans and vegetarians. However, it should be noted that the nutritional profile differs significantly from that of cow’s milk, with far less protein. As said earlier, to reap the benefits of oat milk, alternate sources of protein should be incorporated into the daily diet to maintain appropriate protein consumption.
What Are the Drawbacks of Consuming Oat Milk?
Although an allergy to oat milk is conceivable, oats are not a frequent food allergen. One downside of drinking oat milk is that it includes higher total carbohydrates per serving than cow’s milk. This may be an issue for diabetics who limit their carbohydrate consumption to assist in regulating their blood glucose levels.
Comparing oat milk nutrition with different grades of cow’s milk
Is oat milk a good choice for children
Calcium, vitamin D, and protein are essential for children’s growth and development. Oat milk has somewhat more calcium and vitamin D than cow’s milk owing to fortification (added nutrients). However, oat milk contains only approximately 25% of the protein found in cow’s milk or soy milk. This is a cause for worry considering the importance of protein in infant development. A kid with soy or dairy allergy may be able to drink oat milk, but his or her protein intake may need to be supplemented with other foods.
The flavored and sweetened oat milks includes added sugars. It’s never a healthier option to consume too much additional artificial sugar.
Because oat milk is generally more expensive than cow’s milk, families without allergies or other dietary limitations may find cow’s milk to be a more cost-effective source of protein and other nutrients.
Oat milk is not suitable for baby feeding. Breastmilk is the most recommended source of nutrition for infants (newborns). If nursing is not an option, a suitable baby formula must be supplied. If you have any queries concerning newborn and child feeding and nutrition, please see a health expert.
Conclusion
Being one of the few plant-based beverages, oat milk benefits from its high concentration of fiber and light on the calorific count. Oat milk contains protein, fiber, calcium, and riboflavin, among other things. Although oat milk may be a suitable alternative for adults, particularly those with milk and soy allergies or those following a vegan diet. It may not be the best choice for kid growth because of its low protein level.
Citation
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/pdf/FS/FS41900.pdf
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/oat-milk#summary
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/is-oat-milk-good-for-you-a-dietitian-explains-this-trendy-dairy-alternative/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/oat-milk#recipe



Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/de-CH/join?ref=V3MG69RO
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/sv/register?ref=V2H9AFPY
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/zh-TC/join?ref=V3MG69RO
Wow, awesome blog structure! How long have you ever been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The total look of your web site is excellent, as well as
the content material! You can see similar here dobry sklep